Stanislav Mankov
For decades, long-range missile weaponry is one of the main pillars of the strength
and mythology of russian terrorists. Despite paranoid secrecy in these fields of
study and branches of industry, we have enough open data to get a fairly complete
picture of russia’s “advanced” missile weapons. We’ll start with the spoiler: no, we do not see any signs that the rocket attacks will end quickly. Although this is becoming more expensive, more difficult for Russia (and sometimes even less effective), but according to our estimates, russia’s missiles may be enough for at least another 2-3 weeks of shelling 40-60 missiles a day.
How many missiles russia already used against Ukraine ?
According to US DoD, US DoD, as of April 6, 2022, the Russian Federation has used more than 1,400 missiles of various types (already 1,500+ at the time of publication) since the beginning of the open war against Ukraine.
Here we’re going to talk about medium-range cruise missiles, anti-ship missiles, and tactical ballistic missiles, which are launched from ground, sea, and air platforms. Aviation tactical weapons and rockets for multiple rocket launchers require a dedicated article.
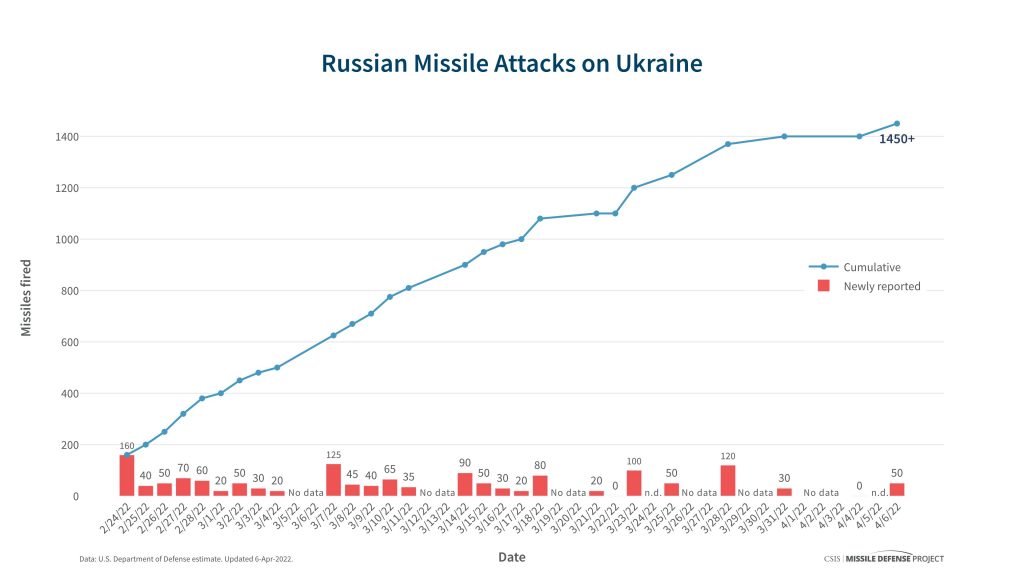
Fifty days after the full-scale war against Ukraine was broke out by russians, it’s possible to track specific trends in missile strikes. Firstly, russia has to perform surprisingly extensive and massive missile strikes due to failed “blitzkrieg”. Secondly, they have to launch extra missiles per target (sometimes military targets) due to the mediocre accuracy of this weaponry. The prepared reserves of ballistic missiles “Iskanders” and cruise missiles “Kalibr” prepared for the “blitzkrieg” have been virtually expended, so russia is forced to:
- deploy older systems (missile system “Tochka-U”, since the third week of the war, e.g.);
- increase step-by-step participation of strategic aircraft in missile strikes. Operations of strategic bombers Tu-22M3, Тu-160 and iconis Тu-95МS cost a lot, in finances and resources, to the enemy;
- use expensive and suboptimal missiles for ground target strikes (since March 18, 2022, Onyx missiles have been launching from the mobile missile complex “Bastion-P” in Crimea).
Similar changes in long-range strike operations of the enemy mean:
- reducing the effectiveness of enemy missile strikes;
- limiting its destruction capabilities;
- dramatically increasing the technical complexity and maintenance cost of missile strikes;
The brief comprehensive chapter about russian missile systems, observed in Ukraine
Generally, the enemy uses a solid bunch of various missile systems to conduct strikes on Ukraine. These systems are divided into two fundamentally distinct categories:
- ballistic missiles – this type of missile follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver a warhead to a predetermined target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered;
- cruise missiles – such missiles are guided missiles that remain in the atmosphere and fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory at an approximately constant speed at the major portion of their flight path. Cruise missiles are aerodynamically controlled (like planes) and designed to deliver a warhead over long distances with high precision in the powered flight.

- Х-555 – subsonic air-launched intermediate-range cruise missile

Soviet/russian subsonic (moving slower than ~ 320 m / s, speed of sound in the air at 5000 m height) strategic cruise missile, used by strategic bombers to perform strikes on warehouses, headquarters, and infrastructure or industry by preloaded coordinates of targets. Modification of Kh-55 / Kh-55SM missiles for the conventional, non-nuclear warhead.
- Warhead mass: up to 400 kg;
- Power plant: turbofan R-95-300 / TRDD-50 engine;
- Speed: 200-230 m / s;
- Operational range: up to 3500 km;
- This type of missile is used exclusively by Tu-22M3, Тu-160 and Тu-95МS – strategic bombers – missile carriers. The most complex and most expensive types of launcher platforms among available to the enemy;
- Optionally toxic if filled up with decilin (engine fuel).
Good news:
- fairly old missiles, the original nuclear-armed missile Kh-55 had been in development since 1971, commissioned in 1984;
- able to attack only stationary targets;
- these missiles are carried by and launched by the most complicated and expensive in operations among all russian military aircraft.
Bad news:
- the enemy has big enough stockpiles of missiles of this type. The minimum estimated amount is ~ 600 pieces Kh-555. After the collapse of the USSR Ukraine got nearly 1,600 Kh-55 / 55SM as a legacy. These cruise missiles are the same type as the non-nuclear ones, Kh-555. There is unknown how many missiles of these types remain and were converted into non-nuclear cruise missiles Kh-555 in Russia;
- truly long-range system to carry out strikes on any corner of Ukraine far away from its borders;
- the engine uses toxic fuel (optional).
- Х-101 – subsonic air-launched intermediate-range cruise missile
Soviet/russian subsonic (moving slower than ~ 320 m / s, speed of sound in the air at 5000 m height) strategic cruise missile, used by strategic bombers to perform strikes on warehouses, headquarters, and infrastructure or industry by preloaded coordinates of targets.
- Warhead mass: up to 450 kg;
- Power plant: turbofan R-95-300 / TRDD-50 engine;
- Speed: 190-200 m / s;
- Operational range: up to 5500 km;
- This type of missile is used exclusively by Тu-160 and Тu-95МС –
- strategic bombers – missile carriers. The most complex and most expensive types of launcher platforms among available to the enemy;
- Optionally toxic if filled up with decilin (engine fuel).
Good news:
- the estimated amount of these missiles – up to 150-200 pieces, this type is still in the process of deployment;
- powerfully hyped by russian propaganda aged project for all money of the world. Soviet engineers began designing the Kh-101 in the late 1980s, the missile achieved initial operating capability in August 2003, and entered service in 2012;
- able to attack only stationary targets;
- these missiles are carried by and launched by the most complicated and expensive in operations among all russian military aircraft.
Bad news:
- truly long-range system to carry out strikes on any corner of Ukraine far away from its borders;
- its use of radar-absorbing composite material makes the missile challenging to detect;
- the engine uses toxic fuel (optional).
- 9M728/9М729 Iskander-K — subsonic ground-launched intermediate-range cruise missile
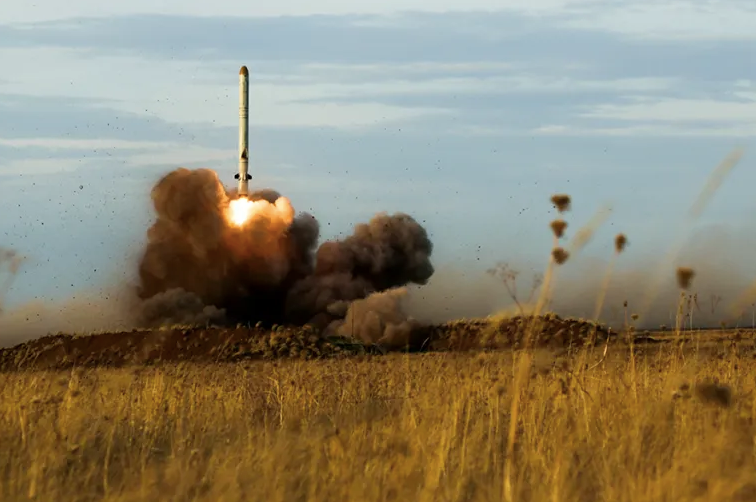

Soviet/russian ground-launched cruise missile based on a mobile 8×8 transporter-erector-launcher(TEL). Despite the proliferation of various names such as R-500 and 9M728/9M729, this is one more missile of family 3M-54 / 3M-14 Kalibr. It entered service in 2007.
- Warhead mass: up to 480 kg;
- Power plant: turbofan TRDD-50 engine, solid propellant rocket booster;
- The open secret was made from an operational range, up to 500 km was declared by russians. Actually it is much larger (based on the dimensions of the rocket and engine specifications) and is up to 2500 km;
- Speed: up to 270 m / s;
- ️The development of this very missile prompted the 2019 U.S. withdrawal from the 1987 INF Treaty. This treaty obliged the United States and the Soviet Union to destroy existing ground-based launchers and stockpiles of cruise and ballistic missiles with a range of 500-5500 km. The development of new launchers and missiles was also banned.
Good news:
- the ground-based launch platform that is more vulnerable, compared to strategic bombers, surface ships, and submarines;
- able to attack only stationary targets;
Bad news:
- the ground-based cruise missile launcher is the cheapest and simplest in operations, compared to strategic bombers, surface ships, and submarines
- long-range weaponry that allows russians to perform missile strikes on Ukraine from the temporarily occupied Crimea or Russian territories.
- 3М-54/3М-14 Kalibr – a family of cruise missiles
A family of Russian cruise missiles with various launch platforms. There are 5-6 kinds of missiles inside the family including anti-ship to anti-submarine and land-strike capable missiles.
In the context of missile strikes on the territory of Ukraine, we are interested in the very 3M-14 missile. This is a subsonic intermediate-range cruise missile able to attack land stationary targets. Launch platforms for 3M-14 are surface ships and submarines. It entered service in 2004.
- Warhead mass: up to 480 kg;
- Power plant: turbofan TRDD-50 engine, solid propellant rocket booster;
- Speed: up to 270 m / s;
- Operational range: up to 2500 km;
Good news:
- The aged project was powerfully hyped by russian propaganda aka “analogovnet”. Initial development of the missile started back in the 80s, survived the USSR, and received a second breath in Russian Federation. Version 3M-14 entered service in late 2004;
- able to attack only stationary targets;
- there are some reliability issues with these missiles.
Bad news:
- long-range weaponry that allows russians to perform missile strikes on Ukraine from any point of the Black Sea or the temporarily occupied Crimea ports.
- P-800/3М55 Onyx, — supersonic universal anti-ship missile
Soviet / russian supersonic (moving faster than ~ 320 m / s, speed of sound in the air at 5000 m height ) universal medium-range missile, sea and coastal based. The missile has been in development since 1983 and was adopted in service in 2002. The primary targets of Onyx are ships. Also, it is capable to attack ground targets. Export modification of this P-800 missile is called “Yakhont”. According to reports, an improved version of this missile, called Onyx-M and an extended up to 800 km range, has been tested since September 2019.
“Bastion-P” coastal missile system with P-800 Onyx missiles is used to perform missile strikes in Ukraine. The complex entered service in 2015.

- Warhead mass: up to 200-250 kg;
- Power plant: ramjet engine, solid propellant rocket booster;
- Speed: up to 680-750 m / s;
- Operational range: up to 300 km;
Good news:
- the smallest warhead among observed missiles of these types;
- one of the most expensive missiles in the enemy’s arsenal – supersonic technologies are difficult and expensive;
- the ground platform that can be detected and destroyed;
- able to attack only stationary land targets;
- relatively short range. From the positions in Crimea, this missile reaches only a few adjacent to Crimea regions.
Bad news:
- cruising supersonic speed of the missile leaves minimal reaction time after launch;
- 9M723 Iskander-M – ground-launched short range ballistic missile
Soviet / Russian solid-propellant single-stage ballistic missile based on a ground mobile platform. “Grandson” of the missile complex “Tochka-U”.
- Warhead mass up to 700 kg;
- Operational range: up to 500 km;
- Speed ~ 2.4 km / s (burn-out speed)
- Export model this very missile, Iskander-E, performed extremely poorly during the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. According to Nikol Pashinyan, the prime minister of Armenia, only 10% of missile launches were successful.
Good news:
- The aged project was powerfully hyped by russian propaganda aka “analogovnet”: development started in the late ’80s, entered service in 2006;
- the ground-based launch platform that is more vulnerable, compared to strategic bombers, surface ships, and submarines;
- the ballistic missile, with a high (up to 50 km) and predicted trajectory, early detectable one;
- there are some reliability issues.
Bad news:
- the largest warhead among these types of missiles;
- Limited efficiency of air defense systems against ballistic targets.
- Kh-47M2 Kinzhal — air-launched short range ballistic missile

Russian solid-propellant single-stage air-launched ballistic missile from MiG-31К and Тu-22М3М. Powerfully hyped “hypersonic” weapon, one of the six wunderwaffe, according to Putin’s speech in 2018.. In fact, this wunderwaffe is an ordinary ballistic missile, the same type as the 9M723 Iskander missile. By the way, a huge bunch of ballistic missiles is hypersonic (capable to move 5 times faster than sound in the air).
- Warhead mass up to 700 kg;
- Operational range: up to 500 km;
- Speed ~ 2.4 km / s (burn-out speed).
Good news:
- powerfully hyped “hypersonic wunderwaffe” for intimidation. Nearly a dozen of Kinzhal-capable aircraft with several dozens of missiles – enough for media war, not for the real one.
- air-launched ballistic missiles – one of the most “efficient” ways to waste money because of the huge operational costs of Kinzhal-capable aircrafts
- the ballistic missile, with a high (up to 50 km) and predicted trajectory, early detectable one;
Bad news:
- the largest warhead among the missiles used by russians (similar to Iskander). It was reported, this very missile struck the Retroville shopping mall in Kyiv on the evening of March 20, 2022;
- the Kinzhal-capable aircraft performs launches in the safe zone and is unreachable for Ukraine’s air-defence or fighters;
- the aircraft is a rapid and maneuverable launch platform for the ballistic missile;
- limited efficiency of air defense systems against ballistic targets
- 9M79М Tochka-U — tactical ballistic missile
Soviet ground-based solid-propellant single-stage ballistic missile on a road-mobile platform.
- Warhead mass up to 482 kg;
- Operational range: up to 120 km;
Good news:
- this is an old missile system, that entered service in the far 1975 and became obsolete because of the 9K720 Iskander-M in the russian army. However, it was deployed again during the full-scale russian invasion of Ukraine due to the lack of Iskander missiles;
- short operational range;
- the ground-based launch platform that is more vulnerable, compared to strategic bombers, surface ships, and submarines;
- the ballistic missile, with a high (up to 50 km) and predicted trajectory, early detectable one.
Bad news:
- a significant amount of missiles in the enemy’s stockpiles.
How many missiles does russia has?
Talking about missile statistics, we’ve to distinguish between a complete missile miss, a collateral missile hit, and an actual missile hit.
So, the complete missile miss case is about critical technical failures or the shooting down of a missile by air defense or fighters.
The collateral missile hit is some damage to a random target. For example, the planned target of the missile strike was a military factory. However, missiles hit some resident buildings nearby.
The actual missile hit is damage or destruction specific target as was planned prior to the missile launch.
According to the information of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of Ukraine on March 24, 2022, less than 40% of the enemy missile launches achieved at least the collateral missile hit and we had the possibility to report hits&damage. Obviously, the amount of the actual missile hits has to be lower and classified at the moment.
The infographic does not specify, but likely, the anti-ship P-800 “Onyx” and 9M728 “Iskander-K” cruise missiles are included in the “Kalibr” chunk, and the X-47M2 “Kinzhal” missiles are folded with the ballistic missiles “Iskanders” block.

Using data from the US DoD (total number of missiles launched) and the General Staff of the Armed Forces (number of missiles hit), it is possible to make valid assumptions on how many missiles were used in the period from 24.02.2022 to 06.04.2022, by types:
- Kalibr cruise missiles – 560;
- Iskander ballistic missiles – 540 pieces;
- KH-555 / KH-101 cruise missiles – 300 pieces;
- Tochka-U missiles type – 50 pieces.
Talking about the total amount of missiles,
available to the enemy on 24.02.2022, one or another type, it is possible to make valid assumptions based on public information and analysis of missile launch trends :
Some of these assumptions are:
1) for example, about the Kalibr cruise missiles;
It was reported, according to, Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu, that in 4 months of this year their army received 48 Caliber missiles in April 2019. This info gives us an annual production rate of ~ 150 pieces/year.
The Kalibr missile family includes 6 types: two types of naval-based anti-ship missiles, two types of anti-submarine torpedo-missiles, and two types of land-attack missiles – 3M14 and 9M728, naval and ground-based, respectively.
Only the last two types of missiles are used by the enemy to launch missile strikes on Ukraine.
Trials of the missile were completed by the 3M14 in 2004, and the 9M728 missile completed its tests in 2007. Serial production of the product usually begins only after the completion of its trials.
Therefore, given the annual production rate for the missile family, knowing the number of types within the Kalibr family and the start date of mass production for each of the missiles, it is possible to calculate the estimated number of 3M14 and 9M728 missiles produced : 540 and 450, respectively.
In total, about 990 land-attack missiles were in stockpiles and available to the enemy before the full-scale attack on Ukraine, of which ~ 560 the enemy already has launched to date.
Estimated actual stock of cruise missiles type 3M14 and 9M728 – 430 pieces.
2) the paragraph about “Iskander” ballistic missiles;
There isn’t public information about the production rates of Iskander ballistic missiles. However, the minimum estimated number of ballistic missiles is double ammunition for each of 152 available road-mobile launchers Iskander-M, ie 608 missiles.
Already launched 540 “Iskanders” allow us to obtain estimated actual stock of ballistic missiles about 68 pieces to date. This is the very reason the enemy is forced to deploy obsolete Tochka-U.
The estimated number of air-launched ballistic missiles Kh-47M2 “Kinzhal” about several dozen pieces has an insignificant effect on the overall picture.
3) the one about Kh-555/Kh-101 cruise missiles;
Estimation of the number of cruise missiles X-555 / X-101 complicated by legacy secrecy since Soviet times. These missiles are carried and launched only by strategic bombers Tu-160 and Tu-95MS (also by literally a couple of “modern” Tu-22M3M), which are part of the strategic nuclear arsenal of Russia. The main weapons of these bombers are nuclear-capable air-launched intermediate-range cruise missiles Kh-55, Kh-55SM and Kh-102.
The minimum estimated number of conventional Kh-555 is about ~ 600 missiles, as a secondary ammunition type for strategic bombers.
It is reported that Kh-101 cruise missiles are still in the deployment phase to date. So given the number of strategic missile carriers Tu-160, we can estimate the number of Kh-101 cruise missiles approximately 100-200 pieces.
Despite nearly 300 cruise missiles of these two types already launched by the enemy, at least 400-500 missiles of Kh-555 and Kh-101 are available to russia, according to the minimum estimation.
4) In the scale of the missile strikes all around Ukraine, the number of P-800 missiles (operational range up to 300 km) and Point-U (operational range up to 120 km) is out of scope.
Conclusions
- We see no sign that shelling will end soon. Based on the minimum estimate of the available and residual stockpiles of these missile weapons, we cannot expect a russian missile shelling to end soon.
- russia can shell Ukraine at least next 2 to 3 weeks with 40 to 60 missiles daily. The available estimated stockpiles of missile weaponry allows russia shell Ukraine at least for extra two or three weeks, as powerful as 40-60 missiles daily;
- Yes, it becomes more expensive for russia. The cost of missile strikes is skyrocketing for russia. Increasing amount operations of strategic bombers to launch cruise missiles means an enormous amount of resources. The cheapest, easiest to maintain ballistic and cruise missile carriers are ground-based missile systems. The most expensive and most complex launch platforms to maintain are aircrafts;
- Russia is running out of missiles for the Iskanders, and about half of the cruise calibers left of those prepared for attack prior to February 24. According to our estimates, the stockpiles of ballistic Iskanders for the “blitzkrieg” war are almost exhausted, about half of the Kalibr missiles remains, so russia is forced to use more expensive and less effective weapons – Tochka-U and Onyx missiles
- The deployment of Tochka-U instead of Iskander reduces the effectiveness of russian missile strikes. In the same way as the strikes of land targets by supersonic anti-ship P-800 “Onyx” missiles , which are more expensive and carry a weaker warhead than the 3M-14 “Kalibr” missile ;
- russia is also trying to involve strategic aircraft more intensively in missile strikes. The use of Tu-22M3, Tu-160 and Тu-95МS, costs russia a considerable “penny”, financially and resourcefully;
- extra vigilance, smart dispersion of resources and stockpiles, and air defense should stay Ukraine’s priorities in the nearest future with daily missile strikes.
On February 24, Russia attacked Ukraine. We continue to follow the development of the situation. If you have information about Russian troops movement or any other information you want to share with us, email us via [email protected] or text in telegram on @JavelinSt. For particularly sensitive data – reach out, we will send more encrypted channels.
You can also join the project, volunteer, author or support the project. Here you can find out how.
